Adapting to Change
Over recent years, climate change has been a big concern in the UK. Exhaust emissions from road transport contributed to a large number of UK greenhouse gas emissions (GHG emissions).
Regulations are becoming increasingly strict to combat the amount of GHG emissions emitted from road transport. Car manufacturers are having to make adaptations to the designs of their vehicles to meet the stringent limits.
One method of reducing exhaust emissions is the use of after-treatment devices. The majority of modern vehicles are designed to incorporate an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system. But, what is an EGR...?
What is an EGR valve?
Within modern internal combustion engines, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) is a method to control Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) emissions, produced as a by-product during the combustion process.
Air from the environment, mostly a combination of Oxygen and Nitrogen, combines with fuel and ignites inside the combustion chamber, temperatures increase and produce NOx emissions.
The EGR system works by returning a small portion of exhaust gas to the engine's combustion chambers through the intake manifold, lowering combustion temperatures and therefore reducing the amount of NOx emitted.
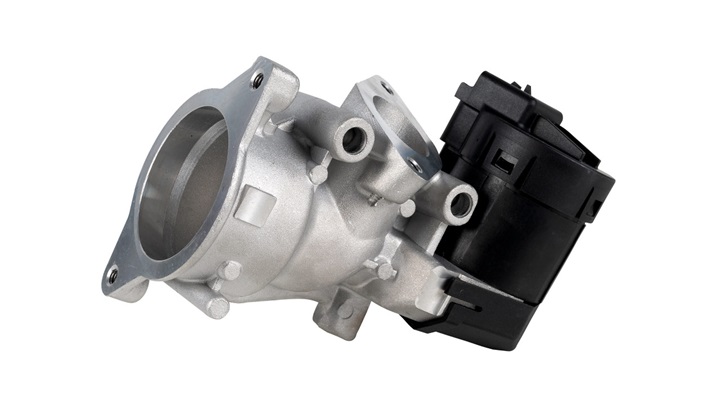
The EGR valve is the main component of the EGR system and it's normally closed. It connects the exhaust manifold to the intake manifold and is controlled by either a vacuum or a built-in electric step motor. The function of the EGR valve is to control the flow of exhaust gas being recirculated depending on the engine load.
Nitrogen Oxide (NOx)
Nitrogen oxides are emissions produced as a by-product from the process of combustion, Nitrogen and Oxygen gases in the air react during combustion, especially at high temperatures.
NOx is a major component of smog and can have detrimental affects on human health as well as well as ecosystems and agricultural crops.
Therefore, incorporating EGR systems into the design of a car is important with regards to lowering harmful emissions to save the environment and have a positive impact on human health.
How does an EGR valve work?
The majority of modern vehicles incorporate EGR valves into their design to reduce NOx emissions and therefore meet stringent emissions regulations. EGR systems recycle a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber, where it combines with fresh intake air.
This lowers the amount of Oxygen and increases the water vapour content to the combustion mixture which reduces the peak combustion temperature. Because more NOx is created as peak combustion temperature rises, the EGR valve effectively reduces the amount of NOx produced by the engine.
The EGR valve begins working once the engine has started, attained the correct operating temperature and the vehicle's speed increases. Gradually, the EGR valve regulates the flow of exhaust gases.
Once the vehicle slows down and the engine stops, the EGR valve will return to its closed position and prevent the flow of exhaust gases.
Carbon deposits and clogged EGR valves
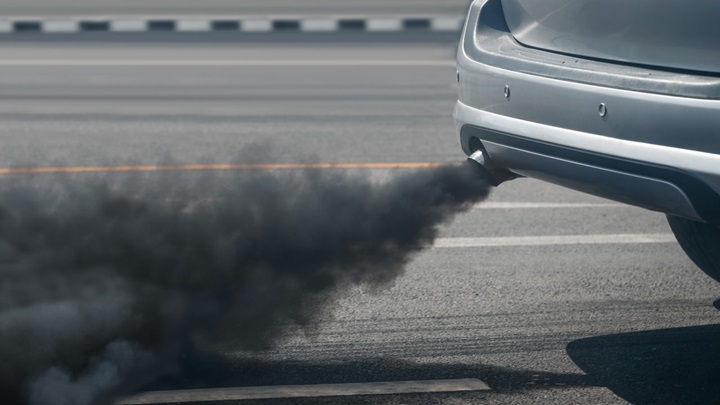
A frequent problem with the EGR valve is sticking due to a build up of carbon deposits. In worst cases, the EGR valve and EGR passages can be completely blocked, preventing the process of recirculating the exhaust gases.
Clogged EGRs are often the cause of black smoke escaping the exhaust, in addition to increased fuel consumption or reduced performance. If the EGR valve fails to open or close, the engine warning light will illuminate on the dashboard.
A strong odour of fuel smelt from inside the vehicle is also a sign of a failing EGR valve as more hydrocarbons will be emitted through the exhaust due to the increase in fuel consumption. The smell is easily noticeable due to its irritating nature, which can actually be harmful to human health.
EGR valve and an MOT test
In the past, car owners attempted to remove EGR valves and Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) from their vehicles to avoid costly repairs.
However, for Euro 6 Emissions Standards compliant vehicles it has now been stated by the Department for Transportation that removing the EGR valve or DPF is illegal as the vehicle will no longer be compliant with the road vehicle regulations.
Vehicles will also fail their MOT test due to emission levels emitted and owners can face an astounding £1,000 fine for removing the EGR valve or diesel particulate filter.
Frequently Asked Questions
It will all depend on the make and model of car. The labour costs will usually be higher than the part itself and will all depend on complexity of the model in question. If you need a quote for an EGR valve or replacement for your car, contact your preferred Evans Halshaw retailer.
While a car can run without an EGR valve, your car will be harming the environment significantly. If it causes the car to emit more emissions than the legal limit, it could also cause an MOT failure.
The most common cause of EGR failure are deposits building up over a period of time.
A rough idle, poor performance, increased fuel consumption, frequent stalling or an engine management light could be symptoms of a faulty EGR valve.
Concerned about your vehicle's EGR valve?
An EGR valve is definitely a positive addition to vehicles in terms of reducing harmful NOx emissions, despite their expensive repair costs.
If you think you're experiencing a faulty EGR valve you can book in for a free vehicle health check at your nearest Evans Halshaw retailer.
Related Articles
-
Guide: How to Safely Change a Car Wheel
02 Feb 2024
-
Guide: How to Top Up Your Car's Washer Fluid
30 Aug 2023
-
Car Valeting Tips From The Experts
26 Jun 2023